Delete Nodes And Return Forest
第14天。
今天的题目是Delete Nodes And Return Forest:
Given the root of a binary tree, each node in the tree has a distinct value.
After deleting all nodes with a value in to_delete, we are left with a forest (a disjoint union of trees).
Return the roots of the trees in the remaining forest. You may return the result in any order.
Example 1:
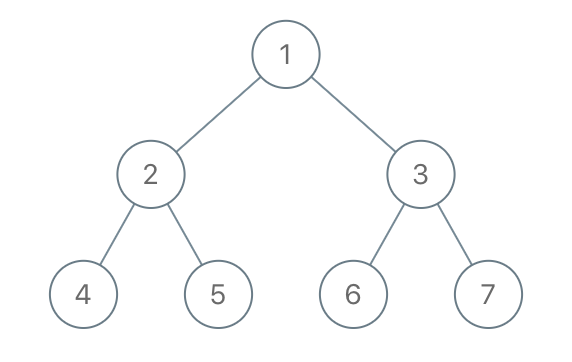
1 | Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], to_delete = [3,5] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree is at most
1000. - Each node has a distinct value between
1and1000. to_delete.length <= 1000to_deletecontains distinct values between1and1000.
这道题的题意很简单,就是要通过删节点来把分割树,关键的问题是,删除一个节点既需要对子节点进行处理,还要在父节点中删除对应的指针,为了方便,我们这里采用后续遍历的方法来实现:
先递归调用函数,使得子树中的节点已经完成遍历和删除,然后通过返回值来判断该子节点是否需要删除,如果需要删除,则将对于的指针置空。然后在判断当前节点是否需要删除,就将非空的子节点插入到返回数组中(全局变量)。
还有一点就是,因为节点的值在1-1000间,所以我们可以用一个长度为1000的数组来加快对要删除节点的判断。
代码如下:
1 | vector<TreeNode *> res; |